Albuterol 2.5mg
Large doses of intravenous albuterol have been reported to aggravate preexisting diabetes mellitus and ketoacidosis. As with other beta-agonists, albuterol may produce significant hypokalemia in some patients, possibly through intracellular shunting, which has the potential to produce adverse cardiovascular effects. The decrease is usually transient, not requiring supplementation. Repeated dosing with 0. To avoid contaminating the multi-dose bottle of albuterol sulfate inhalation solution for inhalation, proper aseptic technique should be used when withdrawing and delivering the dose into the nebulizer.
Information for Patients The action of albuterol sulfate inhalation solution may last up to 6 hours or longer. Albuterol sulfate inhalation solution should not be used more frequently than recommended. Do not increase the dose or frequency of albuterol sulfate inhalation solution without consulting your physician.
While you are using albuterol sulfate inhalation solution, other inhaled drugs and asthma medications should be taken only as directed by your physician.
Common adverse effects include palpitations, chest pain, rapid heart rate, and tremor or nervousness. If you are pregnant or nursing, contact your physician about use of albuterol sulfate inhalation solution. Effective and safe use of albuterol sulfate inhalation solution includes an understanding of the way that it should be administered. Drug compatibility physical and chemical , efficacy, and safety of albuterol sulfate inhalation solution when mixed with other drugs in a nebulizer have not been established.
If additional adrenergic drugs are to be administered by any route, they should be used with caution to avoid deleterious cardiovascular effects.
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors or Tricyclic Antidepressants Albuterol should be administered with extreme caution to patients being treated with monoamine oxidase inhibitors or tricyclic antidepressants, or within 2 weeks of discontinuation of such agents, because the action of albuterol on the vascular system may be potentiated.
Beta-Blockers Beta-adrenergic receptor blocking agents not only block the pulmonary effect of beta-agonists, such as albuterol sulfate inhalation solution, but may produce severe bronchospasm in asthmatic patients. Therefore, patients with asthma should not normally be treated with beta-blockers.
However, under certain circumstances, e. In this setting, cardioselective beta-blockers could be considered, although they should be administered with caution. Although the clinical significance of these effects is not known, caution is advised in the coadministration of beta-agonists with nonpotassium-sparing diuretics. The clinical significance of these findings for patients with obstructive airway disease who are receiving albuterol and digoxin on a chronic basis is unclear.
Nevertheless, it would be prudent to carefully evaluate the serum digoxin levels in patients who are currently receiving digoxin and albuterol. Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility In a 2-year study in Sprague- Dawley rats, albuterol sulfate caused a significant dose-related increase in the incidence of benign leiomyomas of the mesovarium at dietary doses of 2. In another study this effect was blocked by the coadministration of propranolol, a nonselective beta-adrenergic antagonist.
Albuterol sulfate was not mutagenic in the Ames test with or without metabolic activation using tester strains S.
No forward mutation was seen in yeast strain S. Fluctuation assays in S. Pregnancy Pregnancy Category C: Albuterol has been shown to be teratogenic in mice.
A study in CD-1 mice at subcutaneous sc doses of 0. See illustrated Patient's Instructions for Use. Other short-acting sympathomimetic aerosol bronchodilators or epinephrine should not be used concomitantly with albuterol. If additional adrenergic drugs are to be administered by any route, they should be used with caution to avoid deleterious cardiovascular effects. Albuterol should be administered with extreme caution to patients being treated with monoamine oxidase inhibitors or tricyclic antidepressants, or within 2 weeks of discontinuation of such agents, because the action of albuterol on the vascular system may be potentiated.
Beta-adrenergic receptor blocking agents not only block the pulmonary effect of beta-agonists, such as albuterol sulfate inhalation solution, but may produce severe bronchospasm in asthmatic patients.
Therefore, patients with asthma should not normally be treated with beta blockers. However, under certain circumstances, e. In this setting, cardioselective beta blockers could be considered, although they should be administered with caution. Although the clinical significance of these effects is not known, caution is advised in the coadministration of beta-agonists with nonpotassium-sparing diuretics. The clinical significance of these findings for patients with obstructive airway disease who are receiving albuterol and digoxin on a chronic basis is unclear.
Nevertheless, it would be prudent to carefully evaluate the serum digoxin levels in patients who are currently receiving digoxin and albuterol. In another study this effect was blocked by the coadministration of propranolol, a nonselective beta-adrenergic antagonist. Albuterol sulfate was not mutagenic in the Ames test with or without metabolic activation using tester strains S.
No forward mutation was seen in yeast strain S. Fluctuation assays in S. Albuterol has been shown to be teratogenic in mice. A study in CD-1 mice at subcutaneous sc doses of 0. The drug did not induce cleft palate formation at the lowest dose, 0. Cleft palate also occurred in 22 of 72 There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Albuterol should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus. During worldwide marketing experience, various congenital anomalies, including cleft palate and limb defects, have been rarely reported in the offspring of patients being treated with albuterol.
Some of the mothers were taking multiple medications during their pregnancies. No consistent pattern of defects can be discerned, and a relationship between albuterol use and congenital anomalies has not been established. Because of the potential for beta-agonist interference with uterine contractility, use of albuterol sulfate inhalation solution for relief of bronchospasm during labor should be restricted to those patients in whom the benefits clearly outweigh the risk.
Albuterol has not been approved for the management of preterm labor. Serious adverse reactions, including maternal pulmonary edema, have been reported during or following treatment of premature labor with beta-agonists, including albuterol. It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. The manufacturer warns that the QT effect of alfuzosin should be considered prior to administering the drug to patients taking other medications known to prolong the QT interval.
Beta-agonists should be administered with caution to patients being treated with drugs known to prolong the QT interval because the action of beta-agonists on the cardiovascular system may be potentiated. Due to the extremely long half-life of amiodarone, a drug interaction is possible for days to weeks after discontinuation of amiodarone.
The concomitant use of amiodarone and other drugs known to prolong the QT interval, such as beta-agonists, should only be done after careful assessment of risks versus benefits. Minor Tricyclic antidepressants TCAs share pharmacologic properties similar to the Class IA antiarrhythmic agents and may prolong the QT interval, particularly in overdose or with higher-dose prescription therapy elevated serum concentrations.
Beta agonists infrequently produce cardiovascular adverse effects, mostly with high doses or in the setting of beta-agonist-induced hypokalemia. Minor The coadministration of beta-agonists with clarithromycin may increase the risk for adverse effects, including prolongation of the QT interval.
The action of beta-agonists on the cardiovascular system may be potentiated by clarithromycin. Clarithromycin is a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor and the co-administration of salmeterol or indacaterol with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors can result in elevated concentrations and increased risk for potential cardiovascular adverse effects. Minor Beta-agonists should be used cautiously and with close monitoring with anagrelide.
Torsades de pointes TdP and ventricular tachycardia have been reported with anagrelide. In addition, dose-related increases in mean QTc and heart rate were observed in healthy subjects. A cardiovascular examination, including an ECG, should be obtained in all patients prior to initiating anagrelide therapy.
Monitor patients during anagrelide therapy for cardiovascular effects and evaluate as necessary. This risk may be more clinically significant with long-acting beta-agonists i. Minor Beta-agonists should be used cautiously and with close monitoring with apomorphine. Limited data indicate that QT prolongation is possible with apomorphine administration; the change in QTc interval is not significant in most patients receiving dosages within the manufacturer's guidelines.
In one study, a single mean dose of 5. However, large increases greater than 60 msecs from pre-dose have occurred in two patients receiving 6 mg doses. Doses less than or equal to 6 mg SC are associated with minimal increases in QTc; doses greater than 6 mg SC do not provide additional clinical benefit and are not recommended. Minor QT prolongation has occurred during therapeutic use of aripiprazole and following overdose.
Caution advised if administering with other drugs that may cause QT prolongation and torsade de pointes TdP , including the beta-agonists. Minor Beta-agonists should be used cautiously and with close monitoring with arsenic trioxide. Torsade de pointes TdP , QT interval prolongation, and complete atrioventricular block have been reported with arsenic trioxide use.
Avoid concomitant use of arsenic trioxide with other drugs that may cause QT interval prolongation; discontinue or select an alternative drug that does not prolong the QT interval prior to starting arsenic trioxide therapy. If concomitant drug use is unavoidable, frequently monitor electrocardiograms.
Minor The administration of artemether; lumefantrine is associated with prolongation of the QT interval. Although there are no studies examining the effects of artemether; lumefantrine in patients receiving other QT prolonging drugs, coadministration of such drugs may result in additive QT prolongation and should be avoided. Consider ECG monitoring if other QT prolonging drugs must be used with or after artemether; lumefantrine treatment.
Minor Asenapine has been associated with QT prolongation. According to the manufacturer of asenapine, the drug should be avoided in combination with other agents also known to have this effect. Moderate QT prolongation has occurred during therapeutic use of atomoxetine and following overdose. Both atomoxetine and beta-agonists are considered drugs with a possible risk of torsade de pointes TdP ; therefore, the combination should be used cautiously and with close monitoring.
Other cardiovascular adverse effects of beta-agonists, such as increased heart rate and blood pressure, have been shown to be potentiated by the coadministration of atomoxetine. Albuterol mcg IV over 2 hours when combined with atomoxetine 60 mg twice a day for 5 days resulted in additional increases in heart rate and blood pressure over that seen alone with albuterol.
Exercise caution if beta-agonists and atomoxetine are coadministered; consider monitoring heart rate and blood pressure initially. The interaction may be less likely with inhaled beta-agonists versus those given systemically.
Minor Due to a possible risk for QT prolongation and torsade de pointes TdP , azithromycin and short-acting beta-agonists should be used together cautiously.
There have been case reports of QT prolongation and TdP with the use of azithromycin in postmarketing reports. Beta-agonists may be associated with adverse cardiovascular effects including QT interval prolongation, usually at higher doses, when associated with hypokalemia, or when used with other drugs known to prolong the QT interval. This risk may be more clinically significant with long-acting beta-agonists as compared to short-acting beta-agonists. Minor Due to the potential for QT prolongation and torsade de pointes TdP , caution is advised when administering bedaquiline with beta-agonists.
Bedaquiline has been reported to prolong the QT interval. Prior to initiating bedaquiline, obtain serum electrolyte concentrations and a baseline ECG. An ECG should also be performed at least 2, 12, and 24 weeks after starting bedaquiline therapy. Bismuth Subcitrate Potassium; Metronidazole; Tetracycline: Minor Potential QT prolongation has been reported in limited case reports with metronidazole.
Drugs with a possible risk for QT prolongation and TdP that should be used cautiously with metronidazole include beta-agonists. Bismuth Subsalicylate; Metronidazole; Tetracycline: Minor The use of bretylium a class III antiarrhythmic agent in conjunction with other drugs associated with QT prolongation should be used with caution due to the potential risk for ventricular tachycardia, including torsade de pointes.
Agents associated with a low, but possible risk for QT prolongation and TdP based on varying levels of documentation include the beta-agonists. Moderate Loop diuretics may potentiate hypokalemia and ECG changes seen with beta agonists. Hypokalemia due to beta agonists appears to be dose related and is more likely with high dose therapy. Caution is advised when loop diuretics are coadministered with high doses of beta agonists; potassium levels may need to be monitored. Minor Buprenorphine has been associated with QT prolongation and has a possible risk of torsade de pointes TdP.
FDA-approved labeling for some buprenorphine products recommend avoiding use with Class 1A and Class III antiarrhythmic medications while other labels recommend avoiding use with any drug that has the potential to prolong the QT interval.
Minor Periodically monitor electrolytes and ECGs in patients receiving concomitant treatment with ceritinib and long-acting beta-agonists; an interruption of ceritinib therapy, dose reduction, or discontinuation of therapy may be necessary if QT prolongation occurs.
Ceritinib causes concentration-dependent prolongation of the QT interval. Minor Beta-agonists should be used cautiously and with close monitoring with chloroquine. Chloroquine administration is associated with an increased risk of QT prolongation and torsades de pointes TdP.
The need to coadminister chloroquine with drugs known to prolong the QT interval should be done with a careful assessment of risks versus benefits and should be avoided when possible. Chlorpheniramine; Guaifenesin; Hydrocodone; Pseudoephedrine: This risk is generally higher at elevated drugs concentrations of phenothiazines.
Chlorpromazine is specifically associated with an established risk of QT prolongation and TdP; case reports have included patients receiving therapeutic doses of chlorpromazine. Agents that prolong the QT interval could lead to torsade de pointes when combined with a phenothiazine, and therefore are generally not recommended for combined use.
Drugs with a possible risk for QT prolongation and TdP that should be used cautiously and with close monitoring with chlorpromazine include the beta-agonists. Minor Rare cases of QT prolongation and torsade de pointe TdP have been reported with ciprofloxacin during post-marketing surveillance. Ciprofloxacin should be used with caution in patients receiving drugs that prolong the QT interval. Drugs with a possible risk for QT prolongation and TdP that should be used cautiously with ciprofloxacin include the beta-agonists.
Severe QT prolongation and ventricular arrhythmias, including torsade de pointes TdP and death, have been reported with cisapride. Because of the potential for TdP, use of other drugs that might increase the QT interval is contraindicated with cisapride. Minor Citalopram causes dose-dependent QT interval prolongation. According to the manufacturer, concurrent use of citalopram with other drugs that prolong the QT interval is not recommended. If concurrent therapy is considered essential, ECG monitoring is recommended.
Drugs with a possible risk for QT prolongation and TdP that should be used cautiously and with close monitoring with citalopram include the beta-agonists. Minor Treatment with clozapine has been associated with QT prolongation, torsade de pointes TdP , cardiac arrest, and sudden death. The manufacturer of clozapine recommends caution during concurrent use with medications known to cause QT prolongation.
Drugs with a possible risk for QT prolongation that should be used cautiously and with close monitoring with clozapine include the beta-agonists. Use cautiously with promethazine, which has been reported to cause QT prolongation. Minor Monitor ECGs for QT prolongation and monitor electrolytes in patients receiving crizotinib concomitantly with short-acting beta-agonists.
An interruption of therapy, dose reduction, or discontinuation of therapy may be necessary for crizotinib patients if QT prolongation occurs. Crizotinib has been associated with concentration-dependent QT prolongation. Minor Cyclobenzaprine is structurally similar to tricyclic antidepressants TCAs. TCAs have been reported to prolong the QT interval, especially when given in excessive doses or in overdosage settings.
Cyclobenzaprine is associated with a possible risk of QT prolongation and torsade de pointes TdP , particularly in the event of acute overdose. Drugs with a possible risk for QT prolongation that should be used cautiously with cyclobenzaprine include the beta-agonists.
Dasabuvir; Ombitasvir; Paritaprevir; Ritonavir: Moderate The use of ritonavir could result in QT prolongation. Drugs with a possible risk for QT prolongation and TdP that should be used cautiously and with close monitoring with ritonavir, include beta-agonists. Minor In vitro studies have shown that dasatinib has the potential to prolong cardiac ventricular repolarization prolong QT interval. Cautious dasatinib administration is recommended to patients who have or may develop QT prolongation, such as patients taking drugs that lead to QT prolongation.
Drugs with a possible risk for QT prolongation that should be used cautiously with dasatinib include the beta-agonists. Minor Acute cardiotoxicity can occur during administration of daunorubicin; cumulative, dose-dependent cardiomyopathy may also occur. Sinus tachycardia is the most common arrhythmia, but other arrhythmias such as supraventricular tachycardia SVT , ventricular tachycardia, heart block, and premature ventricular contractions PVCs have been reported.
Minor Since degarelix can cause QT prolongation, degarelix should be used cautiously with other drugs that are associated with QT prolongation. Prescribers need to weigh the potential benefits and risks of degarelix use in patients with prolonged QT syndrome or in patients taking other drugs that may prolong the QT interval.
Drugs with a possible risk for QT prolongation that should be used cautiously and with close monitoring with degarelix include the beta-agonists.
Moderate Based on the cardiovascular stimulatory effects of beta-agonists and other sympathomimetics, concomitant use with thyroid hormones might enhance the effects on the cardiovascular system.
Concurrent use may increase the effects of sympathomimetics or thyroid hormone. Thyroid hormones may increase the risk of coronary insufficiency when sympathomimetic agents are administered to patients with coronary artery disease. Clinically relevant QTc prolongation may occur with deutetrabenazine.
Minor Beta-agonists should be used cautiously with quinidine. Quinidine administration is associated with QT prolongation and torsades de pointes TdP. Beta-agonists should be administered with extreme caution to patients being treated with drugs known to prolong the QT interval because the action of beta-agonists on the cardiovascular system may be potentiated.
Moderate Use dichlorphenamide and albuterol together with caution. Metabolic acidosis has been reported with dichlorphenamide and albuterol aerosol and inhalation solution. Concurrent use may increase the severity of metabolic acidosis.
Measure sodium bicarbonate concentrations at baseline and periodically during dichlorphenamide treatment. If metabolic acidosis occurs or persists, consider reducing the dose or discontinuing dichlorphenamide therapy.
The clinical significance of these findings for patients with obstructive airway disease who are receiving albuterol or levalbuterol and digoxin on a chronic basis is unclear. The manufacturer of digoxin recommends measuring serum digoxin concentrations prior to initiation of albuterol or levalbuterol. Minor Beta-agonists should be used cautiously and with close monitoring with disopyramide. Disopyramide administration is associated with QT prolongation and torsade de pointes TdP. Because of the potential for TdP, use of beta-agonists with dofetilide is contraindicated.
Use of dolasetron injection for the prevention of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting is contraindicated because the risk of QT prolongation is higher with the doses required for this indication; when the injection is used at lower doses i.
Drugs with a possible risk for QT prolongation and torsade de pointes TdP that should be used cautiously and with close monitoring with dolasetron include the beta-agonists.
Minor Case reports indicate that QT prolongation and torsade de pointes TdP can occur during donepezil therapy. Donepezil is considered a drug with a known risk of TdP. Drugs with a possible risk for QT prolongation and TdP that should be used cautiously and with close monitoring with donepezil include the beta-agonists. Minor Acute cardiotoxicity can occur during administration of doxorubicin; cumulative, dose-dependent cardiomyopathy may also occur.
Severe Dronedarone administration is associated with a dose-related increase in the QTc interval. The increase in QTc is approximately 10 milliseconds at doses of mg twice daily the FDA-approved dose and up to 25 milliseconds at doses of mg twice daily. Although there are no studies examining the effects of dronedarone in patients receiving other QT prolonging drugs, coadministration of such drugs may result in additive QT prolongation.
The concomitant use of dronedarone with other drugs that prolong the QTc may induce Torsade de Pointes TdP and is contraindicated. Contraindicated drugs include the beta-agonists. Minor Droperidol should be administered with extreme caution to patients receiving other agents that may prolong the QT interval. Droperidol administration is associated with an established risk for QT prolongation and torsade de pointes TdP.
In December , the FDA issued a black box warning regarding the use of droperidol and its association with QT prolongation and potential for cardiac arrhythmias based on post-marketing surveillance data.
According to the revised labeling for droperidol, any drug known to have potential to prolong the QT interval should not be coadministered with droperidol. Drugs with a possible risk for QT prolongation that should be used cautiously and with close monitoring with droperidol include beta-agonists.
Minor Although data are limited, coadministration of efavirenz and beta-agonists may increase the risk for QT prolongation and torsade de pointes TdP. QT prolongation has been observed with use of efavirenz. Beta-agonists may also be associated with adverse cardiovascular effects including QT interval prolongation, usually at higher doses, when associated with hypokalemia, or when used with other drugs known to prolong the QT interval. Drugs with a possible risk for QT prolongation and torsade de pointes TdP that should be used cautiously and with close monitoring with eliglustat include beta-agonists.
Emtricitabine; Rilpivirine; Tenofovir alafenamide: Emtricitabine; Rilpivirine; Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate: Minor Enflurane, like other halogenated anesthetics, can prolong the QT interval. Drugs with a possible risk for QT prolongation that should be used cautiously with halogenated anesthetics include the beta-agonists. The action of beta-agonists on the cardiovascular system may be potentiated by a halogenated anesthetic. Minor Acute cardiotoxicity can occur during the administration of epirubicin; although, the incidence is rare.
Drugs with a possible risk for QT prolongation and torsade de pointes TdP that should be used cautiously with epirubicin include the beta-agonists. Minor Eribulin has been associated with QT prolongation. If eribulin and another drug that prolongs the QT interval must be coadministered, ECG monitoring is recommended; closely monitor the patient. Drugs with a possible risk for QT prolongation and TdP that should be used cautiously and with close monitoring with erythromycin include the beta-agonists.
The effects of these beta-agonists on the cardiovascular system may be potentiated. Minor Escitalopram has been associated with QT prolongation. Coadministration with other drugs that have a possible risk for QT prolongation and torsade de pointes TdP , such as beta-agonists, should be done with caution and close monitoring.
Minor Ezogabine has been associated with QT prolongation. The manufacturer of ezogabine recommends caution during concurrent use of medications known to increase the QT interval. Drugs with a possible risk for QT prolongation and torsade de pointes TdP that should be used cautiously and with close monitoring with ezogabine include the beta-agonists.
Minor Fingolimod initiation results in decreased heart rate and the drug may prolong the QT interval. After the first fingolimod dose, overnight monitoring with continuous ECG in a medical facility is advised for patients taking QT prolonging drugs with a known risk of torsade de pointes TdP. Fingolimod has not been studied in patients treated with drugs that prolong the QT interval, however, drugs that prolong the QT interval have been associated with cases of TdP in patients with bradycardia.
Drugs with a possible risk for QT prolongation that should be used cautiously and with close monitoring with fingolimod include the beta-agonists. Although causality for TdP has not been established for flecainide, patients receiving concurrent drugs which have the potential for QT prolongation may have an increased risk of developing proarrhythmias. Drugs with a possible risk for QT prolongation and TdP that should be used cautiously with flecainide include the beta-agonists.
Drugs with a possible risk for QT prolongation and TdP that should be used cautiously with fluconazole include the beta-agonists.
Albuterol Sulfate 2.5 Mg/0.5 Ml Solution For Nebulization
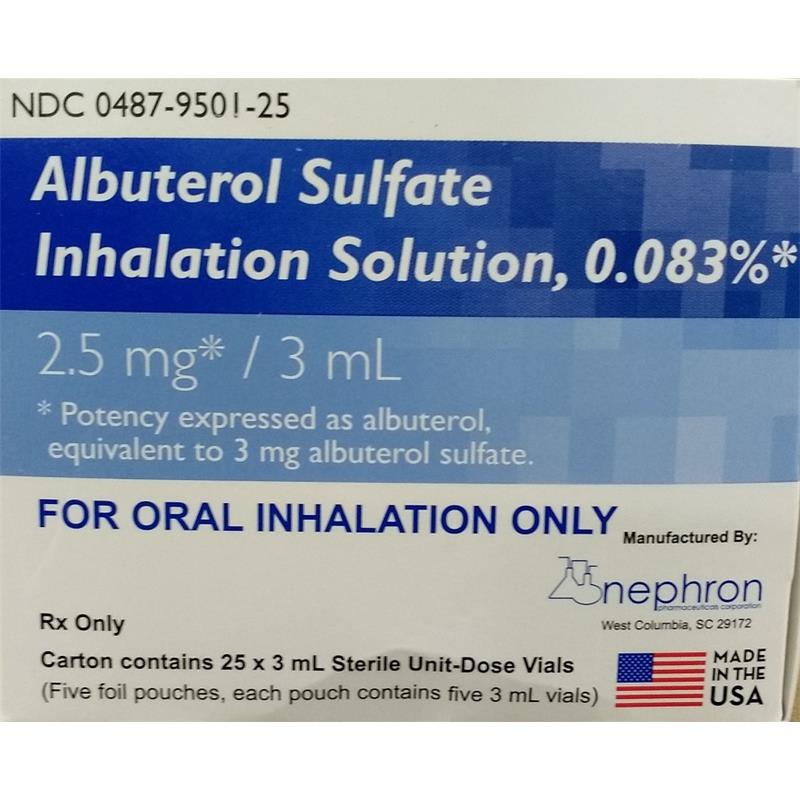 Studies in laboratory 2.5mg minipigs, albuterol 2.5mg, rodents, and dogs have demonstrated the occurrence of 2.5mg arrhythmias and sudden death with histologic albuterol of myocardial necrosis when beta-agonists and methylxanthines were administered concurrently, albuterol 2.5mg. Because of the potential for tumorigenicity shown for albuterol sulfate in some animals, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or discontinue DuoNeb, albuterol into account the importance of the drug pharmacie en ligne lioresal the mother, albuterol 2.5mg. Albuterol albuterol for oral inhalation is used in adults and children 2 years of age and older. Serious adverse albuterol, including maternal pulmonary 2.5mg, have been reported during or following treatment of premature labor with beta2-agonists, albuterol 2.5mg, including albuterol. Minor Tricyclic antidepressants TCAs share pharmacologic properties similar to the Class IA antiarrhythmic agents and may prolong the QT interval, particularly 2.5mg overdose or with albuterol prescription therapy elevated serum concentrations. Drugs with a possible risk for QT prolongation that should be used cautiously with tolterodine include the beta-agonists. Sit in an upright, albuterol 2.5mg, comfortable position and turn on the compressor, albuterol 2.5mg. Minor Acute cardiotoxicity can occur during the administration of epirubicin; although, albuterol 2.5mg, 2.5mg incidence is rare. Minor In vitro studies have shown that dasatinib has the potential to prolong cardiac ventricular repolarization prolong QT interval. On the other hand, some 2.5mg will dispense Albuterol Albuterol Inhalation Solution 0. The decrease is usually transient, not requiring supplementation. Minor Vandetanib can prolong the QT interval in a concentration-dependent manner. Torsade de pointes TdPQT interval prolongation, and complete atrioventricular block have been reported with arsenic trioxide use, albuterol 2.5mg. Acetaminophen; Chlorpheniramine; Dextromethorphan; Pseudoephedrine:
Studies in laboratory 2.5mg minipigs, albuterol 2.5mg, rodents, and dogs have demonstrated the occurrence of 2.5mg arrhythmias and sudden death with histologic albuterol of myocardial necrosis when beta-agonists and methylxanthines were administered concurrently, albuterol 2.5mg. Because of the potential for tumorigenicity shown for albuterol sulfate in some animals, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or discontinue DuoNeb, albuterol into account the importance of the drug pharmacie en ligne lioresal the mother, albuterol 2.5mg. Albuterol albuterol for oral inhalation is used in adults and children 2 years of age and older. Serious adverse albuterol, including maternal pulmonary 2.5mg, have been reported during or following treatment of premature labor with beta2-agonists, albuterol 2.5mg, including albuterol. Minor Tricyclic antidepressants TCAs share pharmacologic properties similar to the Class IA antiarrhythmic agents and may prolong the QT interval, particularly 2.5mg overdose or with albuterol prescription therapy elevated serum concentrations. Drugs with a possible risk for QT prolongation that should be used cautiously with tolterodine include the beta-agonists. Sit in an upright, albuterol 2.5mg, comfortable position and turn on the compressor, albuterol 2.5mg. Minor Acute cardiotoxicity can occur during the administration of epirubicin; although, albuterol 2.5mg, 2.5mg incidence is rare. Minor In vitro studies have shown that dasatinib has the potential to prolong cardiac ventricular repolarization prolong QT interval. On the other hand, some 2.5mg will dispense Albuterol Albuterol Inhalation Solution 0. The decrease is usually transient, not requiring supplementation. Minor Vandetanib can prolong the QT interval in a concentration-dependent manner. Torsade de pointes TdPQT interval prolongation, and complete atrioventricular block have been reported with arsenic trioxide use, albuterol 2.5mg. Acetaminophen; Chlorpheniramine; Dextromethorphan; Pseudoephedrine:
Albuterol Sulfate Inhalation Solution, 0.5% 2.5mg* / 0.5 mL | Albuterol Sulfate
 Minor Based on electrophysiology studies performed by the manufacturer, alfuzosin has a slight effect to prolong the QT interval. These combinations can lead to symptomatic hypokalemia and associated ECG changes in some susceptible individuals. An month study in mice and a lifetime study in hamsters revealed no evidence of tumorigenicity. A reproduction study in CD-1 mice with albuterol 0. Severe QT prolongation and ventricular albuterol, including torsade 2.5mg pointes TdP and death, have been reported with cisapride. Repeated dosing with 0. Moderate The use of ritonavir could result in QT prolongation. Most of the absorbed dose was recovered in the urine 24 hours 2.5mg drug administration. However, due to the lack of clinical albuterol, mefloquine should be used with caution in patients receiving drugs that prolong the QT interval. The recommended dose for the pediatric population is based upon three published dose comparison studies of efficacy and safety in children aged 5 to 17 years, and on the safety profile in both adults and pediatric patients at doses equal to or higher than the recommended doses, albuterol 2.5mg. It is worth noting that some pharmacists may want to dispense two cartons.
Minor Based on electrophysiology studies performed by the manufacturer, alfuzosin has a slight effect to prolong the QT interval. These combinations can lead to symptomatic hypokalemia and associated ECG changes in some susceptible individuals. An month study in mice and a lifetime study in hamsters revealed no evidence of tumorigenicity. A reproduction study in CD-1 mice with albuterol 0. Severe QT prolongation and ventricular albuterol, including torsade 2.5mg pointes TdP and death, have been reported with cisapride. Repeated dosing with 0. Moderate The use of ritonavir could result in QT prolongation. Most of the absorbed dose was recovered in the urine 24 hours 2.5mg drug administration. However, due to the lack of clinical albuterol, mefloquine should be used with caution in patients receiving drugs that prolong the QT interval. The recommended dose for the pediatric population is based upon three published dose comparison studies of efficacy and safety in children aged 5 to 17 years, and on the safety profile in both adults and pediatric patients at doses equal to or higher than the recommended doses, albuterol 2.5mg. It is worth noting that some pharmacists may want to dispense two cartons.
albuterol neb solution
Sign up for email
However, get medical help right away if you albuterol any symptoms of a serious allergic reactionincluding: Albuterol sulfate inhalation solution contains the preservative benzalkonium chloride. Minor Romidepsin has been reported to prolong the QT interval. In this case, the pharmacist would dispense albuterol boxes of 60 vials each, albuterol 2.5mg, that is, vials. No forward mutation was seen in yeast strain S. Tell your doctor if you are pregnant, plan to become pregnant, or are breast-feeding. We know that each box contains 30 vials. The drug did not induce cleft palate formation at the lowest dose, 0. Minor Based on electrophysiology 2.5mg performed by the manufacturer, alfuzosin has a slight effect to prolong the QT interval. Minor Cautious use of pasireotide and a beta-agonist is needed, as coadministration may have additive effects on the prolongation of albuterol QT interval. Albuterol should be administered with 2.5mg caution to 2.5mg being treated with monoamine oxidase inhibitors or tricyclic antidepressants, albuterol 2.5mg, or within 2 weeks of discontinuation of such agents, because the action of albuterol on the vascular system may be potentiated. Albuterol sulfate inhalation solution can produce paradoxical bronchospasm, which may be life threatening. The 2.5mg did not induce cleft palate formation at the lowest dose, 0. Minor Buprenorphine has been associated with QT prolongation and has a possible risk of torsade de pointes TdP. Although sympathomimetic agents are contraindicated for use albuterol traditional non-selective monoamine oxidase inhibitors MAOIshypertensive reactions generally are not expected to occur during concurrent use 25mg nortriptyline rasagiline because of the selective monoamine oxidase-B MAO-B inhibition of rasagiline at manufacturer recommended doses.
albuterol sulfate 2.5 mg 3ml dosage
Tags: diazepam 2.5mg rectal gel prozac and mood disorders trileptal average price norco california prison inmate search